There is a growing need to protect email communication channels. VIPRE security researchers predict a 276% increase in email-distributed malware in 2024. One component that can improve email security is the humble email proxy.
An email proxy is an excellent addition to business security. However, you may be surprised at how easily (and cheaply) you can adopt it for business (or even home) use.

Table of Contents
- What is an Email Proxy
- Why Email Proxies are Important
- Types of Email Proxies
- How to Choose an Email Proxy
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is an Email Proxy?
An email proxy is a gateway through which all email traffic must pass. The email proxy can perform various security checks and filtering processes during the process. That results in a significantly reduced risk of malicious content reaching the user.
How an Email Proxy Works
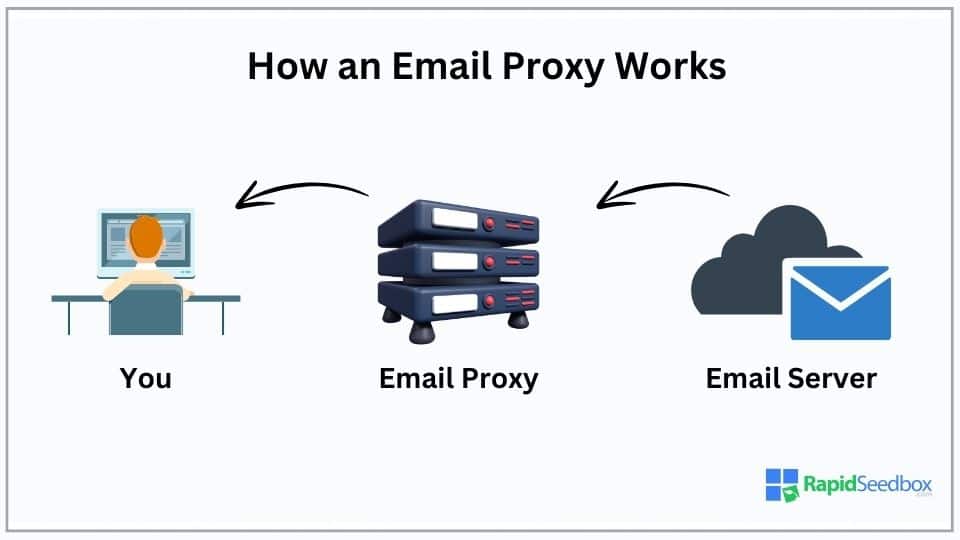
Initially, when an email is sent, it arrives at your email server. The server must be configured to send the email via your email proxy. This crucial step will allow the email proxy to work its magic.
The email proxy applies predefined rules and scanning technologies to inspect the email’s content, attachments, and even the sender’s reputation. Based on this analysis, the email is either passed on to you, quarantined if suspicious, or blocked if harmful.
2. Why Email Proxies are Important
Email today remains one of the fastest and most cost-effective forms of communication. That’s why so many use it. It’s also the reason why email spam and malware continue to rise. Where there is demand, there’s money to be made by cyber criminals.
Email proxies can help in many ways. This includes in:
- Protecting Against Phishing: They are instrumental in identifying and blocking phishing emails, thus safeguarding users from scams or other security compromises.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many organizations today must comply with data protection laws like GDPR and HIPAA. Email proxies help with features like Data Loss Prevention, encryption, and secure email archiving.
- Secure Data Handling: Email proxies can encrypt emails in transit and at rest. That ensures sensitive data is inaccessible to unauthorized users.
- Improved Privacy and Anonymity: Email proxies contribute to user privacy by masking IP addresses and providing secure, anonymous email communication.
- Policy Enforcement: Allow the implementation of organizational policies regarding email use, ensuring all communications adhere to company guidelines.
- Load Reduction: By filtering spam and unnecessary emails, email proxies reduce the load on email servers, enhancing performance and reducing downtime.
Are your business communications unprotected?
Rapidseedbox offers robust and versatile IPv4 and IPv6 proxies. Get free IP rotation and enjoy the benefits of 100% privately owned IP addresses.
————
3. Types of Email Proxies
The effectiveness of an email proxy largely depends on its type and configuration. Each type of email proxy is typically pre-configured to specific needs. Here’s a closer look at the different kinds of email proxies and their roles in email communication.
SMTP Proxies
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) proxies specialize in managing outgoing email traffic. They are essential in preventing your email system from being used to send spam or malicious content. This is done via a careful inspection of each outgoing message.
SMTP proxies ensure that all emails comply with set policies and do not contain harmful links or attachments. This protects the recipient but also safeguards your reputation. The strategic effect is to prevent the possible blacklisting of your domain.
Key Functions
- Filtering and scanning outgoing emails for malware and spam.
- Rate limiting to prevent email flooding and reduce spamming risks.
- Authentication and encryption to secure emails from being intercepted.
Basic SMTP Proxy Usage Guide
- In your email application, configure the SMTP settings to route emails through the SMTP proxy. This typically involves specifying the proxy’s IP address or domain name on the SMTP server.
- Define rules for outgoing emails. This can include attachment types allowed, size limits, and content filters to prevent sensitive information leaks.
- Regularly review the proxy’s logs and adjust policies as necessary.
POP3 and IMAP Proxies
Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3) and Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) proxies focus on the incoming email traffic. They scrutinize every incoming message for threats and unwanted content before it reaches the user’s inbox.
These proxies significantly reduce the risk of phishing attacks, malware infection, and other email-borne threats by providing a protective barrier.
Key Functions
- Scanning attachments and links for malicious content.
- Implementing anti-spam filters to keep unsolicited emails at bay.
- Offering the option to quarantine suspicious emails for further inspection.
Basic POP and IMAP Usage Guide
- Adjust your email client’s POP3 or IMAP settings to route incoming emails through the proxy. This directs email retrieval through the security layer.
- Activate spam filters, malicious content scanners, and phishing protection features in the proxy.
- Ensure your proxy’s security measures are updated with the latest threat definitions.
Webmail Proxies
A webmail proxy is generally designed to secure access to web-based email services. They act as intermediaries between the user’s browser and the webmail server, providing additional security and privacy.
Webmail proxies are particularly useful in public or shared network environments. These environments often see a higher risk of eavesdropping and data theft.
Key Functions
- Enforcing secure connections (HTTPS) to protect data in transit.
- Applying content filters to webmail interfaces to block harmful scripts or content.
- Enhancing privacy by anonymizing user IPs and managing cookies securely.
Basic Webmail Proxy Usage Guide
- Instead of directly logging into your webmail, use the webmail proxy’s URL. It will then securely redirect you to your email service.
- Ensure the proxy is configured to use HTTPS. Doing so will encrypt the data exchanged between your browser and the webmail server.
- Remember to take advantage of features like IP masking and secure cookie management. With these, you can enhance your privacy while using webmail.
Secure Email Gateways
Consider a secure email gateway (SEG) if you require something with iron-clad security. These are comprehensive solutions that combine the functionalities of SMTP, POP3, IMAP, and webmail proxies.
They provide an all-encompassing approach to email security, covering both inbound and outbound traffic. SEGs often have advanced threat detection technologies, including deep content analysis, anti-phishing techniques, and sandboxing.
Key Functions
- Advanced threat protection against malware, phishing, and zero-day attacks.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) to monitor and control sensitive information flow.
- Email encryption to ensure that confidential data remains secure.
Basic SEG Usage Guide
- Deploy the SEG as a central point through which all email traffic, both incoming and outgoing, is routed. This might involve changes to your MX (Mail Exchange) records and email server configurations.
- Set up advanced threat protection measures, data loss prevention policies, and email encryption.
- Inform users about potential email threats and how to recognize them. You can monitor the SEG’s logs and reports to fine-tune policies for this.
Read our comprehensive guide on proxy types to learn more.
4. How to Choose an Email Proxy
Choosing a suitable email proxy can be more complicated than you imagine. The main reason is that you must understand your specific needs and what various proxy services offer. Only then can you try to identify the closest fit.
- Prioritize Encryption: Look for proxies with advanced encryption protocols like SSL/TLS. These protocols encrypt email data during transmission.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Depending on your industry, there may be specific compliance standards (such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX). Thus, ensure that your email proxy can meet these needs with secure archiving, audit trails, and other features.
- Security Features: Look for a solution that provides comprehensive protection. Hence, seek key features like spam filtering, virus and malware scanning, phishing protection, content filtering, and sandboxing for suspicious attachments.
- Advanced Filtering and Analysis: Look for advanced data analysis capabilities like behavioral analysis and threat intelligence integration.
- Scalability and Performance: Assess the solution’s architecture to ensure it can efficiently handle your projected email volumes and user count.
- Management and Usability: An ideal email proxy should be easy to manage and use. Look for intuitive interfaces, comprehensive reporting, and alerting features.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure the email proxy seamlessly integrates with your email infrastructure. That includes email servers, protocols, cloud-based services, etc.
Note: Before finalizing your proxy selection, conduct comprehensive performance testing to evaluate speed, reliability, and network stability. Test factors include latency, download/upload speeds, and load factor performance.
5. Final Thoughts
Understanding and implementing email proxies is essential for business owners seeking to fortify their communication channels. As such, these tools help streamline communications and, more importantly, safeguard sensitive information.
As technology evolves and cyber threats increase, staying ahead of the curve in email security is essential. Due to this, an email proxy may be one cog in the wheel, but it protects you internally and externally against significant digital threats.
6. Frequently Asked Questions
To send an email via a proxy server, you must configure your email client to route outgoing email traffic through the proxy server’s IP address. This requires adjusting your email client’s SMTP settings to specify the proxy server’s address and port number.
Gmail does not natively support a proxy configuration within its web interface. However, you can route Gmail traffic through a proxy by configuring your operating system or using a third-party application or browser extension that supports proxy settings.
DNS for an SMTP server refers to resolving domain names to IP addresses. This means that when sending an email, the SMTP server uses DNS to translate the recipient’s email domain into an IP address, allowing the email to be delivered to the recipient’s mail server.
To connect your email to SMTP, you need to configure your email client or software with the SMTP server settings provided by your email service provider. This typically involves specifying the SMTP server address, port number, authentication method, and encryption protocol.
No, IMAP is not a mail server. Instead, IMAP is an email protocol used by email clients to retrieve emails from a mail server and synchronize them with the client’s local mailbox. Thus, IMAP allows users to access their emails from multiple devices while storing them on the server.
0Comments