In today’s interconnected world, where everything we do leaves behind a trail, it has become increasingly crucial to safeguard our privacy and maintain our anonymity. One of the factors that can expose our identity is our IP address. This means that websites, social media platforms, government authorities, and others have the ability to monitor our activities on a scale.
Naturally, this puts our privacy at risk and allows third parties to gather information about us. It can also restrict our access to content and services. Fortunately, there are methods to hide or fake our IP address (like a proxy or a VPN).
In this guide, we will delve into the concept of anonymity. Show you how you can fake a different IP address in just a few seconds, empowering you to take charge of your online privacy.

Disclaimer: This material has been developed strictly for informational purposes. It does not constitute endorsement of any activities (including illegal activities), products or services. You are solely responsible for complying with the applicable laws, including intellectual property laws, when using our services or relying on any information herein. We do not accept any liability for damage arising from the use of our services or information contained herein in any manner whatsoever, except where explicitly required by law.
Table of contents:
- What is an IP Address and Why Would You Want to Fake It
- The Risks of Not Hiding Your IP Address
- Tools and Methods to Fake Your IP Address
- Conclusion
1. What is an IP Address and Why Would You Want to Fake It?
Before getting into what fake IPs are, let’s initially understand what an IP address actually is.
a. IP address
IP is short for Internet Protocol address, a numerical label that is assigned to every device connecting to the internet or a network. It serves the function of giving a device a unique identifier, which further facilitates communication and exchange of information over the internet. There are two primary types of IP addresses:
IPv4 addresses are constructed out of a sequence of numbers, four sets of numbers, divided by periods. Each of these four sets can range from 0 to 255; therefore, an IPv4 address can look as follows: 192.168.0.1. This was the original IP standard which is still widely utilized today, but with the explosion of connected devices, the number of IPv4 addresses has been depleted.
To replenish the pool of available addresses, IPv6 was introduced. This standard represents an address as eight groups of hexadecimal digits separated by colons. Such an addressing scheme offers a wide pool of potential addresses. An example of an IPv6 address is as follows: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334.
b. Why fake an IP address?
It is crucial to recognize that once an IP address gets exposed, it can potentially be exploited to gather information on a user. Hackers and malicious actors can track someone’s whereabouts and activities through an IP address. This is one of the reasons why users opt to use fake IP addresses.
By using a fake IP address, you can safeguard your online anonymity and show potential hackers that you’re in a different location. This address spoofing can also help in evading online censorship, and surveillance and encrypting your traffic while surfing the web on a public Wi-Fi. These reasons represent only the tip of the iceberg, with usage being flexible and varied.
2. The Risks of Not Hiding Your IP Address

While your IP address may not reveal sensitive information, like your phone number or exact location, hackers can still exploit it to their advantage. If a cybercriminal gains access to your IP address, they can use it for nefarious purposes.
a. How hackers can take advantage of your IP address
They can use your IP address to get an idea of your location, such as the state, city, or zip code you’re in, although they won’t be able to find specific details like your street address. By combining this knowledge with your name or username on social media platforms, hackers can monitor your activities. Gather bits of information from your comments and photos.
This allows them to narrow down the location of your home or workplace, which could potentially lead to crimes like burglary or stalking.
There’s a risk of a hacker launching a DDoS attack against you if they manage to get hold of your IP address. This kind of attack involves the hacker controlling computers to flood your device with traffic, leading to disconnection from the internet and eventual shutdown.
Although the IP address itself doesn’t reveal any information, if it falls into the hands of criminals may use it as a means of verification and employ phishing techniques to trick service providers into revealing sensitive details about you. Moreover, there is a risk that your IP address and other sensitive information could be sold on the web. Each IP address is associated with ports. If you lack sufficient security measures, a hacker who has your IP address can employ various methods to compromise your network and gain control over it.
Once connected to your device successfully, they can take control of it. Potentially steal any stored data. Alternatively, they may infect your device with malware, which allows them to carry out hacking activities undetected.
b. Collecting IPs via trackers
To understand how people interact with their advertising campaigns, online advertisers use methods like cookies, tracking URLs, and tracking pixels in their articles and ads. These trackers collect your IP address, allowing them to target you with spam and ads based on your browsing history and approximate location.
c. IP restrictions
Service providers also have the power to block or blacklist IP addresses. Some online platforms like networks, entertainment sites, or gaming websites may restrict access from regions by banning IP addresses. Moreover, if someone disapproves of your actions or suspects that you have violated their rules, they might decide to add your IP address to a blacklist.
3. Tools and Methods to Fake Your IP Address
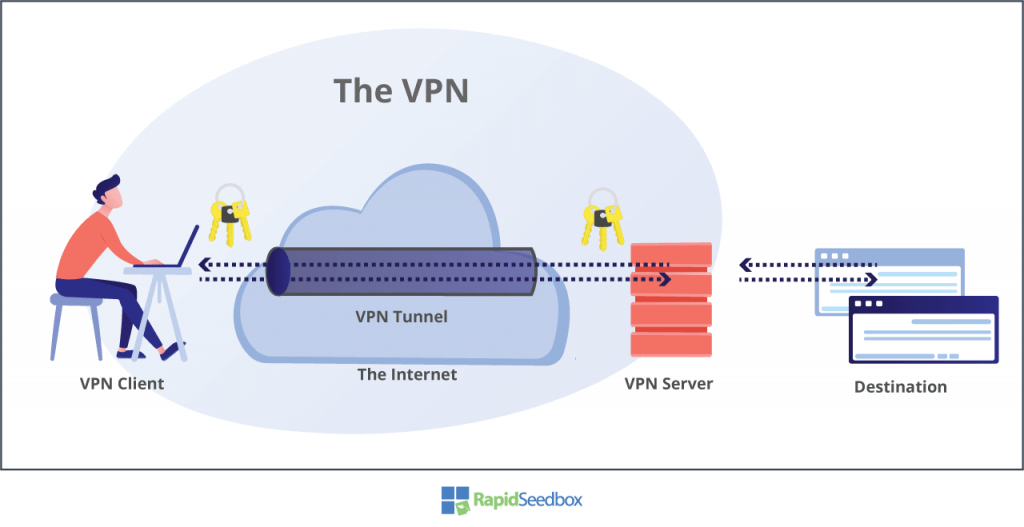
a. How to Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to Fake Your Real IP Address
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a software service that guarantees the transmission of data to and from the Internet. It accomplishes this by redirecting the data through servers, known as VPN servers, located in various locations. These VPN servers encrypt all the information, acting as a mediator between your device and the internet, the VPN server conceals your IP address and virtual location, making it impossible for websites and online applications to identify your identity.
The majority of VPNs operate on a subscription model where users pay a fee to access an array of servers worldwide. Faking your IP address with a VPN service is a simple three-step process:
- Simply sign up for the service
- Download the corresponding apps for your devices, and you’re good to go
- With a few clicks that will turn on the VPN, you can effortlessly conceal your IP address and safeguard your internet traffic
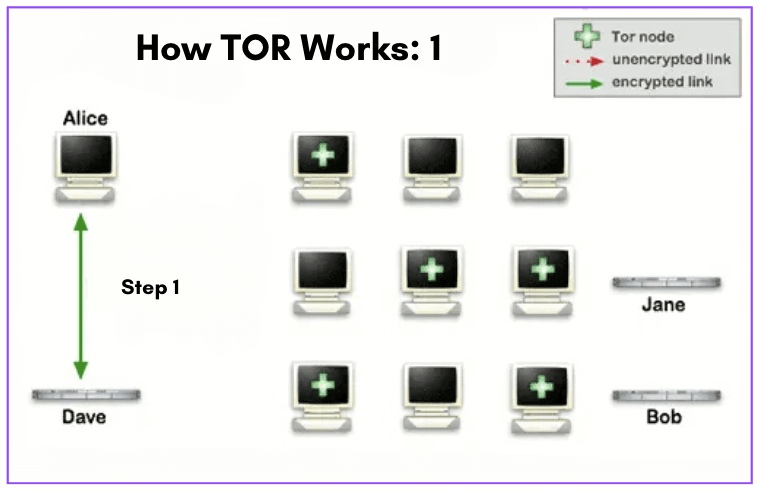
b. Using Tor to Stay Anonymous and Fake Your IP Address
Tor, also referred to as The Onion Router, acts as a distributed network that ensures anonymity by relying on the dedication of volunteers. When you connect to Tor, your internet traffic is routed through a series of volunteer-operated “nodes” that function as servers. Websites can only see the IP address of the exit node, which is the server, in this sequence. The order of these nodes changes with each website visit, making it exceedingly difficult to trace the activity to the IP address.
To make use of Tor effortlessly, you can install the Tor Browser, which works like popular browsers such as Chrome and Firefox and doesn’t require any payment. However, there are some limitations. Tor tends to be slower and isn’t suitable for activities like P2P sharing or streaming; it’s primarily designed for web browsing. Moreover, due to its ability to access websites and the darknet, Tor has been associated with illegal activity. Some websites may block connections from recognized Tor nodes, and your Internet Service Provider might not approve of its usage.
Extra Sources of Information: Is Tor browser safe? And Tor browser review
c. Use a CGNAT Firewall to Fake Your Private IP Address
The main idea of this solution is to allow a number of users, not from one building n but from entire regions, to share one or a smaller pool of public addresses. By implementing CGNAT, ISPs and carriers can improve scalability and accommodate customers using a limited number of public IPs. It’s important to note that CGNAT is a temporary solution as the world gradually transitions to IPv6. Similar to NAT, CGNAT offers a layer of security for internet connections. By converting private IPs into public ones, it strengthens the security of both the connection and the router. It isolates devices within the network and acts as a deterrent against unauthorized access from external sources. This helps protect customers’ devices from attacks targeting public IP addresses.
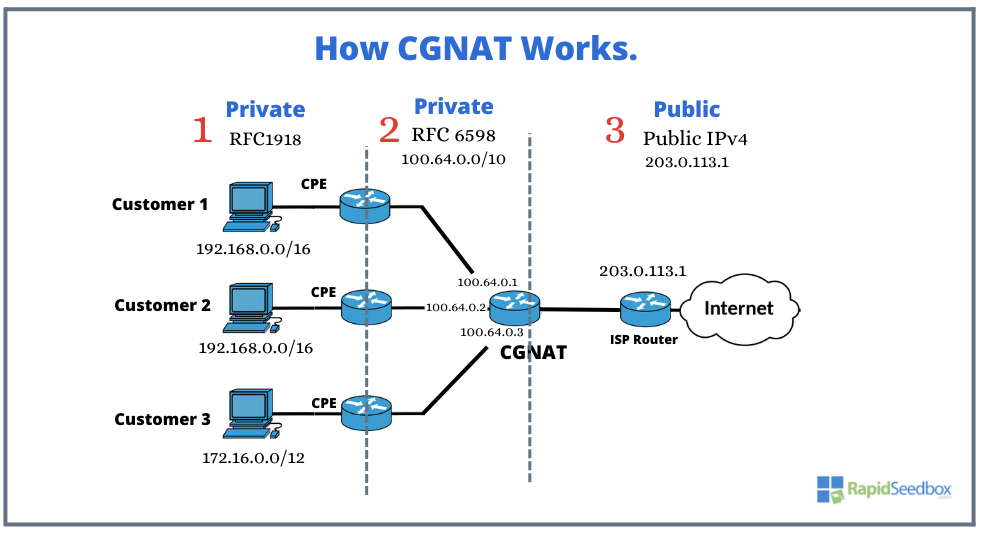
While CGNAT does not serve as a security tool, it does offer the advantage of concealing the internal network and regularly changing your external IP. Its purpose is to enable an ISP to utilize multiple IP addresses for NAT’ing. From a network standpoint, if the attacker is located at the ISP, then yes, they will see the ISP’s IP addresses, and it will be challenging to determine which connections are yours.
Your browser has a unique fingerprint that can be used to track you across various services. In reality, most users prioritize convenience and opt to enable GPS, “login using Google,” and allow scripts from Facebook and Google trackers to run on most websites. By doing so, any protection provided by CGNAT is rendered ineffective. Therefore, employ other security techniques alongside a CGNAT to ensure your security and anonymity (antidetect browsers for example).
d. Use a Proxy to Fake Your IP Address
A proxy, similar to a VPN, acts as a middleman between your device and the internet. If your IP address is revealed, websites and apps only see the IP address of the proxy server. To be more specific, a VPN is technically a type of proxy. However, when we say “proxy,” it usually means SSL, SSH, or SOCKS proxies. Although these types don’t offer the encryption and security that VPNs do, they still hide your IP address from websites. You can configure them in existing applications like your browser or use a third-party app that works similarly to a VPN.
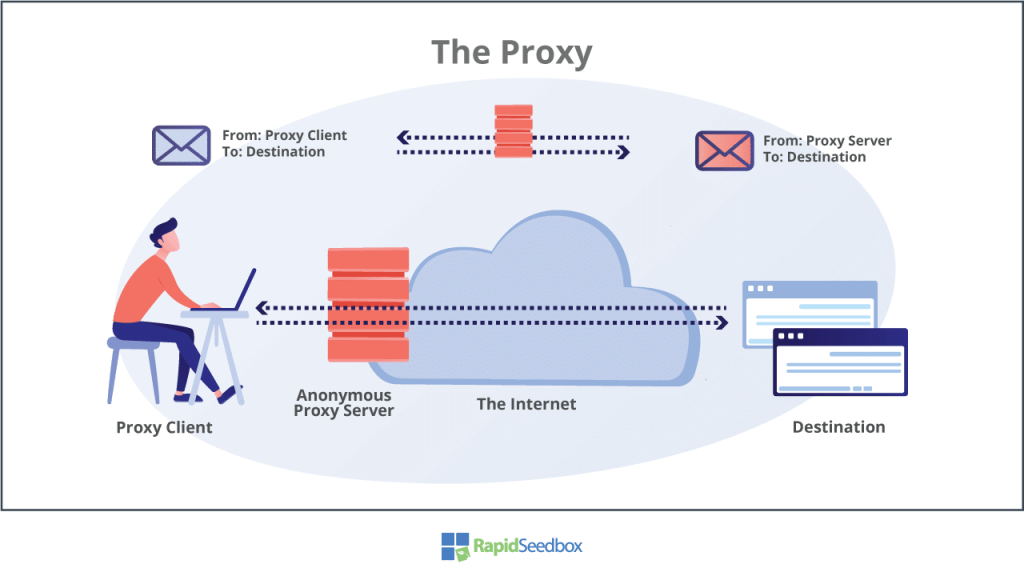
Proxies usually don’t handle DNS traffic. As a result, your website requests are still sent to a third-party DNS server that can detect your IP address. This issue doesn’t occur with VPNs that have leak protection. Also, if the proxy connection drops for any reason, there’s a chance that your real IP might be exposed. Since proxies lack the encryption protocols found in VPNs, they are more susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks. These attacks involve an attacker pretending to be the server in order to steal your data. Some VPN services offer browser extensions for Chrome and Firefox that use HTTPS (SSL) proxies. These extensions effectively secure your browsing activities. However, although these extensions protect your browser, they may not provide the level of security for applications and DNS requests, potentially exposing your IP address.
Want to fake your IP address for better privacy?
Achieve complete anonymity with RapidSeedbox’s secure VPN services. Enjoy fast, private browsing and robust protection to keep your online activities hidden.
4. Conclusion
In today’s era, learning the art of preserving anonymity and the ability to fake your IP address is essential. Understanding what an IP address entails and the risks of not hiding it helps you to protect your privacy effectively.
Using tools like converters for IP addresses, and VPNs, and being mindful when sharing PI, can help you stay anonymous. Thus, taking steps to safeguard your privacy becomes paramount. Embrace the concept of faking an IP address and enjoy the freedom and peace of mind that comes with being in control of your identity.
0Comments