Proxy servers are hugely useful for business and personal use. In this guide, we’ll look at the key differences between IPv4 and IPv6 proxies and why using an IPv6 proxy over an IPv4 proxy could save you a fortune.

Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is a Proxy?
- What Can I Do with a Proxy?
- IP Addresses Explained
- Benefits of IPv6
- Reasons to Choose an IPv6 Proxy
- Reasons to Choose an IPv4 Proxy
- Conclusion
What is a Proxy?
A proxy server is a server application that acts as an intermediary between your computer and external resources. Instead of connecting directly to the resource, all the communication back and forth goes through a third-party proxy server.
The proxy server has long been an important tool in network design to add functionality or solve network routing problems.
A proxy can be public-facing or private-to-private, forwarding or reverse, transparent, anonymous, or high-anonymity, for instance.
For further details on the breadth of proxies available today, we’ve listed all the different types of proxy servers you’ll find, each with its pros and cons. We’ve also created a complete guide to SOCKS5 proxies, one of the most popular types of proxies in use today.
What Can I Do with a Proxy?
Proxies are fundamental to network design because of how useful they can be. Proxies can focus on specific applications, such as HTTP proxies for websites, SMTP proxies for email, and SEO proxies for search engine optimization use. Some of the most common ways to use proxies are to:
Bolster Security
Proxies are useful from a security standpoint because you can use them to hide your company’s internal network structure.
They can be used to limit the type of content your company employees can access, blocking viruses and other malware before it even reaches your network.
Improve Performance
Caching proxies can improve the performance of your applications. By keeping local copies of commonly-accessed resources, proxies reduce the demand on your network.
Proxies can be used to test geo-targeted advertising. By using a proxy in another country, for instance, you can view how advertising will appear to them.
You can use a search engine optimization (SEO) proxy to perform keyword research, rank tracking, and distributed botting. Proxies can be used for web scraping, where you collect data from publicly available sources.
Circumvent IP-based restrictions
Every device connecting to the wider internet has a unique IP (Internet Protocol) address.
Proxies are often used to circumvent website access restrictions that are based on IP address. Sites that limit the purchase of high-value, high-demand items like limited edition sneakers and concert tickets to one per IP address can be circumvented with the use of a proxy, for instance.
Similarly, proxies are often used to access streaming media that are only available to specific regions and bypass government censorship.
Remain Anonymous
Ultimately, because any resource you access online is unable to see your real IP address when you use a proxy, instead seeing only the IP address of the proxy server, their use can help you become anonymous online. You can use proxies to share torrents anonymously, for example.
IP Addresses Explained
When you choose a paid proxy service, you now have the choice between IPv4 and IPv6 proxies. To understand which to choose better, you need to understand their key (IPv4 vs. IPv6) differences.
We briefly discussed IP addresses above. IP addresses are used to identify devices connected to the internet. Every time you connect to the internet via your internet service provider, Wi-Fi, mobile, or even local connection, you receive an IP address. Internet-connected devices cannot communicate with one another without an IP address.
IPv4
Since 1981, IP addresses have been written in the format described in RFC 791. IPv4 addresses are decimal 32-bit addresses divided into four sections. Here’s an example:
49.143.45.133
IPv4 addresses may not exactly trip off the tongue, but they’re still relatively easy for humans to write down, type out, or remember. There’s also support for over 4 billion different IPv4 addresses.
The problem is, we now have more than 4 billion devices vying for these addresses! Internet service providers have had to utilize several workarounds that have stretched the system to its limit.
IPv6
Enter IPv6. IPv6 is the replacement format for IP addresses first introduced in RFC 2460 on June 6, 2012. Instead of the 32-bit IPv4 notation, IPv6 is 128-bit. IPv6 is written in hexadecimal. Here’s an example of a full IPv6 address:
0123:4567:89ab:cdef:0123:4567:89ab:cdef
IPv6 addresses can be shortened in many cases, but they’re still a little harder to read for humans. But IPv6 has many advantages over IPv4, which we’ll look at in the next section.
Benefits of IPv6
IPv6 supports many more devices than IPv4. It solves the biggest problem we’ve hit with IPv4, as it supports 340 undecillion devices, compared to IPv4’s 4 billion. 340 undecillion IP addresses is equivalent to 340 trillion trillion trillion IP addresses.
Better Performance
IPv6 has a simpler header format than IPv4. IPv4 uses 12 header fields, whereas IPv6 only uses 8 header fields. Additional information can be included in extension headers. Since typical routers don’t need to process these extension headers, their job is made easier, so router performance improves with IPv6.
IPv6 uses smaller routing tables and the source device now handles fragmentation rather than the router. Both improvements result in the more efficient and hierarchical routing of traffic.
IPv6 has an integrated system for managing QoS (Quality of Service). QoS is apportioning specific amounts of available bandwidth to different applications sharing the network. While it’s possible to do some QoS on IPv4 networks, it’s baked into IPv6, with specialized fields like flow label and traffic class that ensure bandwidth is used effectively.
Stronger Security
The huge size of the address pool makes for better security by default, as it becomes much more difficult for hackers to brute-force scan through all the possible IP addresses on a network. Even better—IPv6 automatically checks packet integrity and can encrypt traffic at a network level. This makes the use of IPv6 close to the security of using a VPN.
Simpler Network Infrastructure
Because the IPv4 protocol includes so few addresses, we’ve long had to come up with ways to share IP addresses between computers.
One way is through the use of NAT (Network Address Translation), where a router examines each packet entering the local network and decides which device it needs to be sent to. This has certainly extended the life of IPv4, but it slows things down as every packet entering the network needs to be examined and altered.
IPv6 doesn’t use require NAT at all. Not only is this more efficient, but it also makes setting up and maintaining company networks a lot easier.
IPv6 also includes multicasting support by default. This is where a single packet can be sent to multiple devices concurrently. Though this is more of a niche use case, when it’s required, using IPv6 for multicasting is much, much easier to set up than IPv4.
IPv4 vs IPv6 Proxies
When renting a proxy service for any of the types of applications listed above, you can now choose between IPv4 proxies and IPv6 proxies.
Why IPv6 Proxies? Dive In with Rapidseedbox! 🌍
Direct IP Ownership: No middle-man.
24/7 Support: Any time, every day of the week.
Tailor-Made Hosting Solutions
Easy pricing with no hidden fees.
Get IPv6 proxies today to ensure a safer and more cost-effective online course.
———
Reasons to Choose an IPv6 Proxy
Much Lower Price
Arguably the most important benefit of choosing an IPv6 proxy over an IPv4 proxy is that it’s significantly cheaper.
The provider doesn’t have to pay expensive prices for the hotly-contested IPv4 addresses, which lowers costs. And because IPv6 proxies perform better with lower overhead, they cost less to run while delivering comparable or better performance.
Consider an example spend $48 per month on proxies located in the United States.
| IPv4 Proxy | IPv6 Proxy | |
|---|---|---|
| Price | $48/month | $48/month |
| IP addresses | 48 | 1000 |
| Privately owned IPs | Yes | Yes |
| Unlimited bandwidth | Yes | Yes |
| Price per IP address | $1.00 | $0.05 |
While offering comparable features, IPv6 proxies are around 20 times cheaper than IPv4 proxies on a per-address basis.
Not every application needs 1000 IP addresses, though. So, let’s say we only need 100 IPs. Does IPv6 still have an advantage?
| IPv4 Proxy | IPv6 Proxy | |
|---|---|---|
| IP addresses | 100 | 100 |
| Privately owned IPs | Yes | Yes |
| Unlimited bandwidth | Yes | Yes |
| Price per IP address | $1.00 | $0.15 |
| Price | $100/month | $15/month |
Again, IPv6 proxies are much cheaper than IPv4 proxies, even for smaller applications.
Privacy and Anonymity
Many people use proxies to increase their privacy and anonymity. IPv6 addresses are the clear winner here, as communication over IPv6 requires every endpoint to support IPsec.
Clean Addresses
IPv4 addresses being finite means they have a recordable history. Companies offering IPv4 proxies are limited to a certain range of IP addresses, and when they are used over and over, third parties may add them to a list of known proxies and attempt to block them. This can reduce the efficiency of your application.
Because IPv6 addresses are so ubiquitous, this type of proxy list blocking becomes much less effective. IPv6 addresses are often considered to be “virgin,” “clean,” or previously unused, so your applications are much less likely to be detected or blocked.
Performance
As outlined above, IPv6 offers better performance over IPv4, through improved routing, smaller headers, and better QoS support. Because IPv6 proxies perform better, they require fewer resources to run, so they cost less to rent.
Depending on your application, you’ll often get better results from an IPv6 proxy than an IPv4 proxy. This is especially the case if your application is likely to be blocked if it is detected. These improved results directly correlate with an improved return on investment.
Future Proofing
The ubiquitous implementation of IPv6 is inevitable and it’s picking up speed. Using IPv6 for your proxy application means it will continue to work on IPv6 addresses across the internet, whereas restricting your use to IPv4 could have consequences in the future.
The cost of IPv4 addresses should only continue to rise, too, as there is more and more pressure on the limited number of addresses we have now. Starting with IPv6 allows you to bypass this problem altogether.
Reasons to Choose an IPv4 Proxy
Tried-and-True
So, if IPv6 proxies offer so many advantages, why are IPv4 proxies still the norm? The most common reason is that IPv6 has only been around for a decade, whereas IPv4 has been around since close to the birth of the internet. IPv6, therefore, has more of an unknown quality to it, and many proxy users simply haven’t heard of IPv6 or are unaware of its significant advantages.
Ubiquitous Support
One benefit of IPv4 proxies is the widespread support for IPv4. Virtually all new devices that will connect to the internet in some way have IPv6 support, with various laws mandating its support. It’s still in the minority, though.
Google shows that over 40% of users now connect to its services using IPv6, and adoption is increasing at a linear rate. IPv6 migration is continuing at a fair pace.
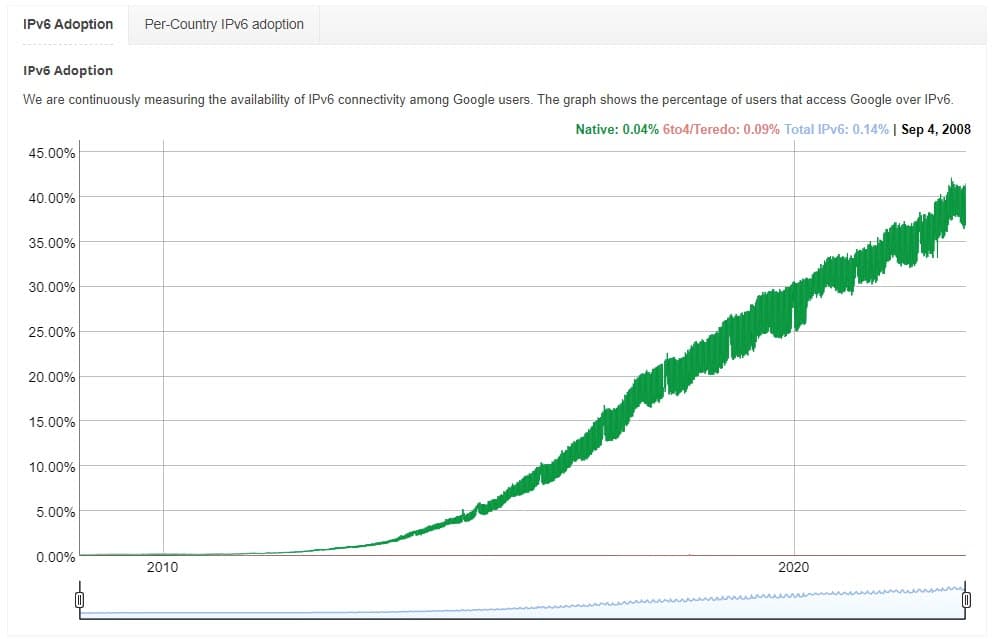
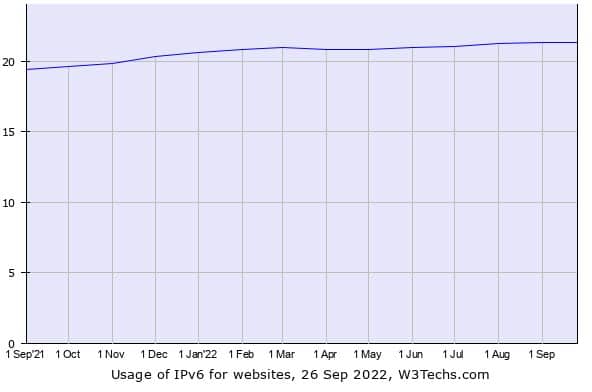
However, making such a fundamental change to how the internet works doesn’t happen overnight. While IPv6 has been the de-facto option for over 10 years, many ISPs (internet service providers), companies, and organizations have a significant amount of older infrastructure that only supports IPv4. IPv6 is only used on around 21.3% of all websites.
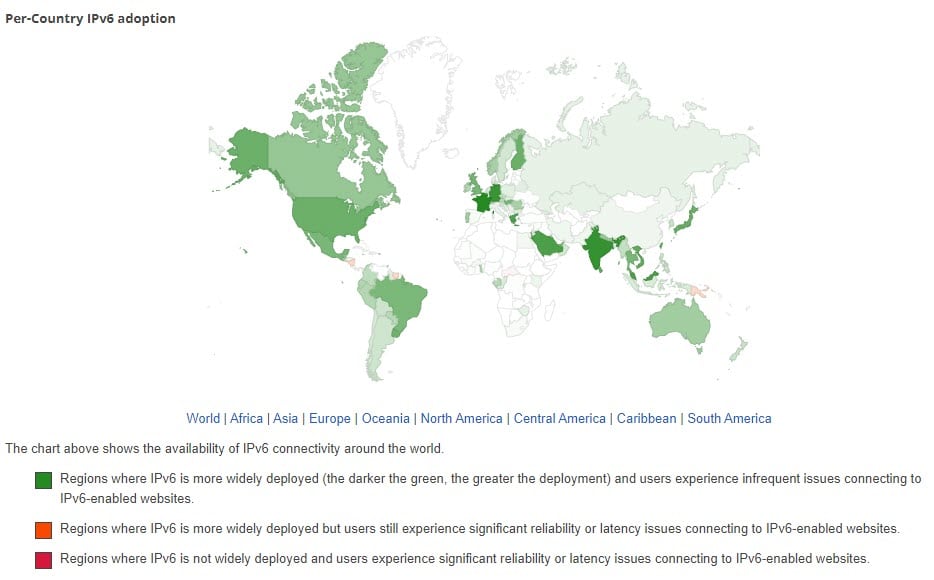
IPv6 adoption varies quite significantly based on country, too. Whether this even matters to you depends on what you plan to use your proxy for. IPv4 proxies do have the advantage that they’re definitely compatible with the majority of systems and protocols used online.
Conclusion
Both IPv4 and IPv6 proxies remain important today, but IPv6 proxies will continue to increase in market share as IPv6 becomes the de-facto protocol in use across the internet.
IPv6 proxies are much cheaper to run than IPv4 proxies. They offer better performance and stronger security, as well as support for more features and a simpler network infrastructure setup.
Consider how much money you could save by choosing an efficient, low-cost IPv6 proxy over an IPv4 proxy when you’re making your choice between the two options.
0Comments