The Internet Protocol (IP) is a critical component of the Internet, acting much like a set of linguistic rules that govern how data is formatted and exchanged online. At the heart of this system are IP addresses, unique numerical labels for each internet-connected device, akin to postal addresses.
These addresses are vital for directing Internet traffic, ensuring data reaches its intended destination efficiently. Without such addresses, the organized transfer of information across the internet would be unfeasible, highlighting their essential role in our everyday online activities.

Table of Content
Basics of IP Addresses
A. IPv6 Addresses
B. IPv4 Addresses
Types and Functions of IP Addresses
1. Private vs. Public IP Addresses
2. Dynamic vs. Static IP Addresses
3. Special-Purpose IP Addresses
The Importance of IP Addresses in Networking
Security Implications of IP Addresses
1. Vulnerabilities Associated with IP Addresses
2. Protecting Your IP Address
3. Best Practices for IP Address Security
4. The Evolving Landscape of IP Security
IP Addresses in the Real World
1. Everyday Internet Use
2. Home and Corporate Networks
3. Online Gaming and Streaming
4. Internet of Things (IoT)
5. E-commerce and Online Transactions
6. Remote Work and Virtual Meetings
Basics of IP Addresses
An IP address in the world of internet technology is like a unique identifier for each device on a network, similar to how every house has a distinct street address. There are two main types of Internet Protocol addresses, known as IPv4 and IPv6, each serving the same fundamental purpose but with different characteristics.
IPv4 Addresses
Think of IPv4 as the original system for house numbering in a vast digital neighborhood. It uses a 32-bit format, which can be visualized as a series of four numbers separated by dots, like “192.168.1.1”. Each number in this sequence can range from 0 to 255. However, just like a small town running out of unique street numbers, the internet outgrew IPv4 due to its limited capacity to offer unique addresses for every device.
IPv6 Addresses
IPv6 addresses emerged as a solution to this problem. Imagine if our town expanded and we needed more elaborate address systems. IPv6 uses a 128-bit format, substantially increasing the number of unique addresses available.
An IPv6 address looks more complex, with eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, like “2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334”. This is like moving from simple house numbers to a combination of numbers and letters for more detailed addresses, accommodating more houses.
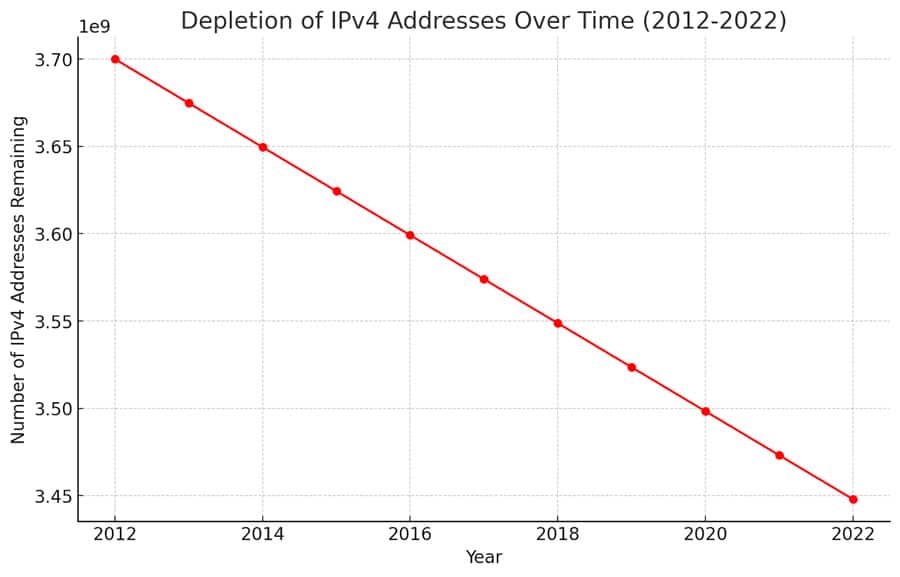
IPv4 Address Decline (2012-2022): The graph shows how the number of IPv4 addresses has been decreasing from 2012 to 2022. Starting from 3.7 billion addresses, about 252 million were used up or given to others during this time. This trend points to the decreasing availability of these addresses.
In essence, understanding the basics of the internet protocol addresses, including the differences between IPv4 and IPv6, helps us appreciate how these digital address systems keep the internet organized and functional. They are the backbone of internet communication, ensuring every device can connect and interact seamlessly in the vast digital landscape.
Types and Functions of IP Addresses

In the vast network of the internet, there are different types of Internet Protocol addresses, each serving a unique purpose. Understanding these types is like knowing the different kinds of mailing addresses – some are for homes, others for businesses, and each has its specific use.
1. Private vs. Public IP Addresses
- Private IP Addresses: These are like home addresses used within a local network, such as your home Wi-Fi. They are not visible on the wider internet and are used for devices to communicate within the same network, like different rooms in a house.
- Public IP Addresses: In contrast, public addresses are like business addresses visible to the world. Assigned by Internet Service Providers, they represent your network’s identity on the Internet, similar to a storefront’s address on a busy street.
2. Dynamic vs. Static IP Addresses
- Dynamic IP Addresses: These are temporary addresses that change each time a device connects to the internet. Think of them as guest passes at a conference, changing for each attendee and each day.
- Static IP Addresses: Unlike dynamic addresses, static ones do not change. They are permanent, akin to a permanent office location in a business complex. They are essential for tasks that require a consistent address, like hosting a website.
3. Special-Purpose IP Addresses
- Loopback and Link-Local Addresses: These are used for specific tasks, like testing network services within a device, similar to using an in-house intercom system.
- Multicast Addresses: Used for broadcasting messages to multiple devices simultaneously, like a public announcement system in a building.
The Importance of IP Addresses in Networking

These addresses in networking are crucial. They not only identify each device but also help manage and direct the flow of internet traffic, much like a mail sorting center ensures each letter reaches its correct destination.
| Type | Characteristics | Typical Use Cases |
| Private IP Address | – Used within a local network (e.g., home, office)- Not routable on the open internet.- Allows multiple devices in the same network to communicate with each other. | – Connecting devices within a home network.- Internal communication in an office network. |
| Public IP Address | – Assigned by Internet Service Providers.- Routable on the open internet.- Unique globally, representing a network’s identity online. | – Accessing the internet.- Hosting a server that is accessible from the internet. |
| Dynamic IP Address | – Changes over time.- Assigned by a DHCP server.- Offers flexibility and reduces the risk of IP address exhaustion. | – Home internet connections.- Devices frequently joining different networks (e.g., smartphones). |
| Static IP Address | – Remains constant.- Manually configured or assigned for long-term use.- Suitable for servers or devices requiring consistent online identity. | – Hosting websites.- Running a mail or FTP server.- Remote access applications. |
Security Implications of IP Addresses

The security aspect of these addresses is akin to understanding the risks and protections of one’s home address in the digital world. Just as revealing your home address can make you vulnerable to certain risks, the visibility of your IP address can expose you to cyber threats.
1. Vulnerabilities Associated with IP Addresses
Cybercriminals can use these addresses to target networks or individual devices. This can lead to unauthorized access, similar to a burglar finding and breaking into your house. Common threats include hacking into your network, disrupting services (like a denial-of-service attack), or even using your IP address for illegal activities.
2. Protecting Your IP Address
To safeguard your digital ‘home,’ there are several strategies:
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Using a VPN is like adding a security system to your home. It hides your actual IP address and encrypts your internet traffic, making it difficult for outsiders to track or intercept your online activities.
- Proxy Servers: A proxy server acts as an intermediary, much like a P.O. box for your internet connection. It helps mask your IP address from the public internet.
- Firewalls and Security Software: Implementing these is akin to having a strong lock on your door. They help protect your network by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on security rules.
3. Best Practices for IP Address Security
Regular updates to security protocols and cautious behavior in sharing personal information online are key to reducing risks. This is similar to keeping your home address private and ensuring your home security measures are up to date.
4. The Evolving Landscape of IP Security
As internet technologies advance, so do the tactics of cybercriminals. Staying informed about the latest security threats and protective measures is crucial, much like staying aware of the latest safety practices in your neighborhood.
While IP addresses are essential for internet connectivity, they also present security risks if not managed properly. Adopting protective measures such as VPNs, proxy servers, and robust security protocols is crucial for safeguarding against potential cyber threats. Just as you would protect your home address and residence, protecting your Internet Protocol address is vital in the digital realm.
IP Addresses in the Real World
The use of IP addresses in our daily lives might not be immediately visible, but it’s as ubiquitous as the use of street addresses in the physical world. Just as street addresses direct mail to our homes, these addresses guide internet traffic to the right devices.
1. Everyday Internet Use
Every online activity, such as visiting a website or sending an email, relies on IP addresses. When you enter a website address, it’s converted into an address that directs your request to the correct server, akin to sending a letter to a specific address.
2. Home and Corporate Networks
In home networks, routers use private IP addresses to connect various devices, much like assigning room numbers in a large house. In corporate environments, they are essential for creating extensive, secure networks for communication and data transfer.
3. Online Gaming and Streaming
These addresses enable online gaming by connecting players worldwide, similar to dialing into a conference call from different locations. Streaming services use these addresses to deliver content and sometimes to restrict it based on geographic location.
4. Internet of Things (IoT)
The burgeoning IoT world, filled with smart devices like thermostats, lights, and voice assistants, relies on such addresses for these devices to communicate with each other, akin to assigning addresses to every appliance in your home.
5. E-commerce and Online Transactions
During online shopping or transactions, IP addresses help in authenticating and securing the process. They can also be used for location-based personalization, like tailoring special offers to your region.
6. Remote Work and Virtual Meetings
IP addresses have become increasingly important for remote work, connecting employees to their company’s networks securely and facilitating virtual meetings, like a phone system connecting various branches of a company.
In conclusion, the internet protocol addresses play a vital role in various aspects of our digital lives, from personal use to professional applications. They ensure the smooth functioning of internet-based activities, making them an invisible yet integral part of our daily digital interactions.
Conclusion
In summary, IP addresses are fundamental to the digital landscape, acting as crucial elements for efficient data flow over the internet. The shift from IPv4 to IPv6 addresses the growing demands of an expanding digital world.
Security considerations surrounding IP addresses underscore the importance of vigilance in our online interactions. As technology advances, particularly with 5G, IoT, and AI, these addresses will play a central role in fostering smarter, more secure networks.
A basic understanding of IP addresses is invaluable, not just for tech professionals but for anyone in our increasingly digital society. As we navigate the digital future, their significance in our online experiences remains paramount.
0Comments